Learn SQL - Web Dev Simplified
Learn SQL - Web Dev Simplified
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language for interacting with relational databases. Below is a quick summary based on the Web Dev Simplified SQL tutorial, with short explanations before each code section.
Before diving into the world of SQL, you’ll need a SQL environment. There are many tools available for this. If you prefer a graphical user interface, you might want to try MySQL Workbench.
In my case, I used MySQL and phpMyAdmin installed via docker. I’ve written a post explaining how to set it up, check it out here: Install MySQL and phpMyAdmin using Docker in Ubuntu.
SQL Basics
This section introduces foundational SQL operations to help you create and interact with relational databases. You’ll learn how to create databases and tables, insert and query data, apply filters, join tables, and perform aggregations.
📘 Create & Select a Database
These commands are essential for setting up and switching between databases.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-- Create a new database
CREATE DATABASE testdb;
-- Delete a database (⚠️ This operation is irreversible)
DROP DATABASE testdb;
-- Select the active database to use
USE testdb;
🧱 Creating Tables
Once your database is created, you can define tables to store structured data. Below is an example for a music catalog containing bands and their albums.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
-- Create a new database for storing record data
CREATE DATABASE record_company;
-- Create a table to store band information
CREATE TABLE bands (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- Add a new column to the bands table (e.g., for country or genre)
ALTER TABLE bands
ADD added_col VARCHAR(255);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-- Create an albums table with a foreign key linking to bands
CREATE TABLE albums (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
release_year INT,
band_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
FOREIGN KEY (band_id) REFERENCES bands(id)
);
✍️ Insert & Query Data
Once tables are defined, use INSERT to add data and SELECT to retrieve it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-- Insert a single band into the bands table
INSERT INTO bands (name)
VALUES ('Iron Maiden');
-- Insert multiple bands in a single command
INSERT INTO bands (name)
VALUES ('Deuce'), ('Avenged Sevenfold'), ('Ankor');
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
-- View all records from the bands table
SELECT * FROM bands;
-- Retrieve only the first two bands
SELECT * FROM bands LIMIT 2;
-- Use aliasing for clearer column names in results
SELECT id AS 'ID', name AS 'Band Name'
FROM bands;
-- Sort bands in descending alphabetical order
SELECT * FROM bands ORDER BY name DESC;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-- Insert multiple albums referencing band IDs
INSERT INTO albums (name, release_year, band_id)
VALUES
('The Number of the Beasts', 1985, 1),
('Power Slave', 1984, 1),
('Nightmare', 2018, 2),
('Nightmare', 2010, 3),
('Test Album', NULL, 3);
🔎 Filtering Data
Use the WHERE clause to filter results based on conditions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-- Retrieve unique album names (no duplicates)
SELECT DISTINCT name FROM albums;
-- Update a specific album's release year
UPDATE albums
SET release_year = 1982
WHERE id = 1;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-- Find albums released before the year 2000
SELECT * FROM albums
WHERE release_year < 2000;
-- Filter by partial name or specific band ID
SELECT * FROM albums
WHERE name LIKE '%er%' OR band_id = 2;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
-- Find albums released between two years
SELECT * FROM albums
WHERE release_year BETWEEN 2000 AND 2019;
-- Show albums with unknown release years
SELECT * FROM albums
WHERE release_year IS NULL;
-- Remove entries with missing release years
DELETE FROM albums
WHERE release_year IS NULL;
🔗 Joining Tables
JOIN operations allow you to query related data across multiple tables.
1
2
3
-- Match albums with their corresponding bands
SELECT * FROM bands
JOIN albums ON bands.id = albums.band_id;
Join Types Overview:
INNER JOIN: Returns only rows with matching values in both tables.LEFT JOIN: Returns all rows from the left table, with matching rows from the right (if any).RIGHT JOIN: Returns all rows from the right table, with matching rows from the left (if any).
📊 Aggregation & Grouping
Aggregate functions let you summarize and group your data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-- Average release year of all albums
SELECT AVG(release_year) FROM albums;
-- Count how many albums each band has (by band ID)
SELECT band_id, COUNT(*) AS album_count
FROM albums
GROUP BY band_id;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-- Count albums per band, showing band names instead of IDs
SELECT
b.name AS band_name,
COUNT(a.id) AS num_albums
FROM bands AS b
LEFT JOIN albums AS a ON a.band_id = b.id
GROUP BY b.id
HAVING num_albums >= 1;
✅ Tip: Use
HAVINGinstead ofWHEREwhen filtering grouped data.
This guide gives you a solid foundation for working with relational databases. As you get comfortable with these commands, you’ll be ready to build more complex queries and applications using SQL.
Exercises
After exploring some basic SQL concepts, this section focuses on a series of exercises primarily proposed by WebDevSimplified. These exercises are designed to be solved after watching the related video or by following along with the previous steps. They are available in his GitHub repository Learn-SQL. In the README.md file, each question is followed by the expected output, you’ll need to figure out the appropriate SQL query to produce that output.
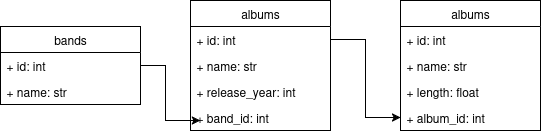
In this post, we share our proposed solutions. First, let’s explore the database schema and set up the environment.
The database contains three tables: bands, albums, and songs. The schema is illustrated in the figure below:
Environment Setup
Make sure you have an environment where you can run SQL queries. As explained earlier, start by creating a database named record_company, then create the schema shown in the figure above.
Once the database is created, insert the required data by running the SQL script provided here.
After completing the setup, you can begin solving the exercises.
Create a
songsTable1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CREATE TABLE songs ( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, length INT NOT NULL, album_id INT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id), FOREIGN KEY (album_id) REFERENCES albums(id) );
Select only the Names of all the Bands
1
SELECT name as "Band Name" FROM bands;
Band Name Seventh Wonder Metallica The Ocean Within Temptation Death Van Canto Dream Theater Select the Oldest Album
1 2 3
SELECT * FROM albums WHERE release_year IS NOT NULL ORDER BY release_year ASC LIMIT 1;
id name release_year band_id 5 …And Justice for All 1988 2 Get all Bands that have Albums
1 2
SELECT DISTINCT b.name as 'Band Name' FROM bands as b JOIN albums as a ON a.band_id = b.id;
Band Name Seventh Wonder Metallica The Ocean Within Temptation Death Van Canto Get all Bands that have No Albums
1 2 3
SELECT DISTINCT b.name as 'Band Name' FROM bands as b LEFT OUTER JOIN albums as a ON a.band_id = b.id WHERE a.id IS NULL;
Band Name Dream Theater Get the Longest Album
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SELECT a.name, a.release_year, SUM(s.length) AS length FROM albums AS a JOIN songs AS s ON a.id = s.album_id GROUP BY a.name, a.release_year ORDER BY length DESC LIMIT 1;
Name Release Year Duration Death Magnetic 2008 74.76666593551636 Update the Release Year of the Album with no Release Year
1 2 3
UPDATE albums SET release_year = 1986 WHERE release_year IS NULL;
Insert a record for your favorite Band and one of their Albums
1 2 3 4 5
INSERT INTO bands (name) VALUES ('Favorite Band Name'); INSERT INTO albums (name, release_year, band_id) VALUES ('Favorite Album Name', 2000, 8);
Delete the Band and Album you added in #8
1 2 3 4 5
DELETE FROM albums WHERE id = 8; DELETE FROM bands WHERE id = 8;
Get the Average Length of all Songs
1
SELECT AVG(length) as "Average Song Duration" FROM songs;
Average Song Duration 5.352472513259112 Select the longest Song off each Album
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT a.name AS "Album", a.release_year AS "Release Year", MAX(s.length) AS "Duration" FROM albums AS a JOIN songs AS s ON a.id = s.album_id GROUP BY a.name, a.release_year;
Album Release Year Duration Tiara 2018 9.5 The Great Escape 2010 30.2333 Mercy Falls 2008 9.48333 Master of Puppets 1986 8.58333 …And Justice for All 1988 9.81667 Death Magnetic 2008 9.96667 Heliocentric 2010 7.48333 Pelagial 2013 9.28333 Anthropocentric 2010 9.4 Resist 2018 5.85 The Unforgiving 2011 5.66667 Enter 1997 7.25 The Sound of Perseverance 1998 8.43333 Individual Thought Patterns 1993 4.81667 Human 1991 4.65 A Storm to Come 2006 5.21667 Break the Silence 2011 6.15 Tribe of Force 2010 8.38333 Get the number of Songs for each Band
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT b.name AS "Band", COUNT(s.name) AS "Number of Songs" FROM bands as b JOIN albums as a ON b.id = a.band_id JOIN songs as s ON a.id = s.album_id GROUP BY b.name;
Band Number of Songs Seventh Wonder 35 Metallica 27 The Ocean 31 Within Temptation 30 Death 27 Van Canto 32